Client Configuration
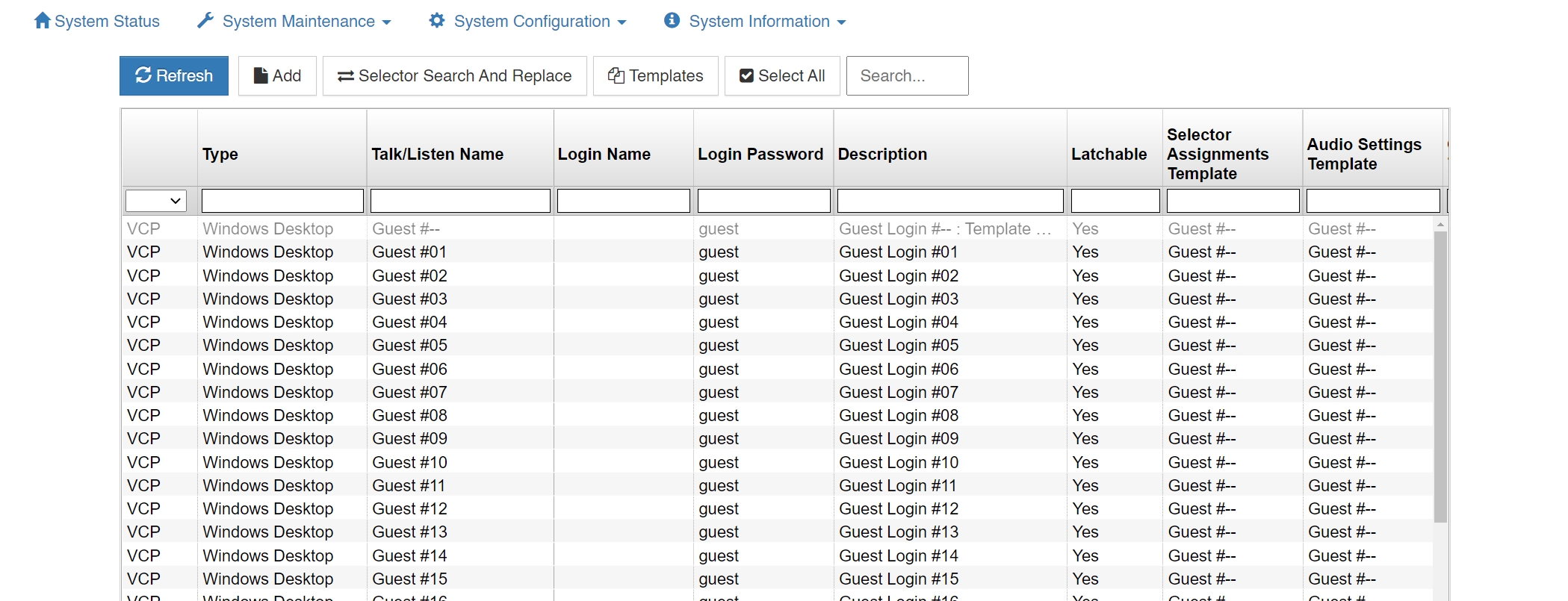
The upper section of the Client Configuration window displays all configured users and devices, log in names, passwords, selector labels, client type, and if the given channel is set as a party line.
Click on a client description name and then Edit to change a parameter, Delete to delete a user or device, Add to create a new client, or Duplicate to copy a client’s settings to a new client.
Client Identification Client Type: Specifies the type of Client that allows the system to modify the internal operational behavior for proper operation of specific, such as VCOM Control Panels, Device Interfaces, Two-Way radios, and SIP devices.
| Category | Client Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: Windows Desktop | For logging into the VCOM (WebRTC) Control Panel on Windows |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: Apple iOS | For logging into the VCOM (WebRTC) Control Panel on iOS |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: Google Android | For logging into the VCOM (WebRTC) Control Panel on Android |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: Apple MAC | For logging into the VCOM (WebRTC) Control Panel on Mac |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: Linux | For logging into the VCOM (WebRTC) Control Panel on Linux |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: TCP-301 | Used for the legacy VCOM TCP-301 Hardware Control Panel |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: TCP-401 | Used for the legacy VCOM TCP-401 Hardware Control Panel |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: TCP-402 | Used for the legacy VCOM TCP-402 Hardware Control Panel |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: TCP-603 | Used for the legacy VCOM TCP-603 Hardware Control Panel |
| VCOM Control Panel | VCP: TCP-701 | Used for the legacy VCOM TCP-701 Hardware Control Panel |
| VCOM Device Interface | VDI: Four-Wire Interface | For logging into the VCOM Device Interface |
| VCOM Device Interface | VDI: 2-Way Radio Interface | For logging into a VCOM Device Interface that is connect to a 2-Way Radio Interface |
| SIP | SIP: Telephone Adapter | Analog Telephony Adapter (FXS): also referred to as an “ATA” enables an analog telephone to function as an IP phone, sitting between your network and analog telephone. |
| SIP | SIP: Telephone Interface | VoIP gateway enables analog phone lines or T-1s with phone service into VCOM |
| SIP | SIP: Softphone | Enables connection to one of the many available softphones designed for Windows, Mac, etc |
| SIP | SIP: Hardphone | Enables a connection to a physical IP phone to VCOM |
| SIP | SIP: Direct IP Trunk | Enables a connection between PBX/SIP Servers and VCOM using IP settings |
| SIP | SIP: Registered Trunk | Enables a connection between PBX/SIP Servers and VCOM using Registration of clients |
| SIP | SIP: Four-Wire Interface | Enables connection of a SIP based Four Wire Interface to transport audio into VCOM |
| VIDEO | VIDEO: HTTP(S) Video Stream | Creates a new video selector. The specified video will be played upon clicking the selector on the WebRTC Control Panel. |
| RTSP | RTSP Audio Tx/Rx Interface | For transmitting and receiving audio via RTSP feed |
| NDI | NDI: Newtek Network Device | For transmitting and receiving audio via NDI feed |
Client Description: The description given to identify the client that is used exclusively in the System Administration application. This allows a complete description of a user (typically first and last name) that cannot otherwise be assigned to the selectors due to space restrictions.
Login Name: The name assigned to a user or device and used to login a Control Panel or Device Interface to the Virtual Matrix. Select ‘Allow Anonymous Login’ to allow a user to login a Control Panel by entering any login name he or she chooses followed by the designated password. The chosen login name will appear on the selector.
Login Password: The password assigned to a user or device and used to login a Control Panel or Device Interface to the Virtual Matrix
Selector Talk/Listen Name: The alphanumeric identifier that appears on Control Panel ‘Talk only’ and ‘Talk/Listen’ selectors.
Selector Listen Only Name: The alphanumeric identifier that appears on Control Panel ‘Listen only’ selectors. This is generally only assigned when a client has split functionality for the audio input and output as with a Program Feed input and IFB output.
Use Domain Authentication (LDAP): This is used when a Client is outside the LAN, and your LAN uses authentication to provide secure connections to remote users. If this option is enabled VCOM queries the OS to retrieve the already authenticated Windows user name. It then uses that name along with an encrypted password unique to that client to log in to the VVM. The VCOM Login Password becomes obsolete because the VCOM Control Panel will only permit login if that Windows User Name has been successfully authenticated. The Use Domain Authentication option must also be checked on the Control Panel. VCOM does not communicate with the Domain Controller.
Options Disable Client Login/Connection: This allows the System Administrator to “turn-off” certain clients when they are not needed to login to the system. Always Show Selector when Off-line: Specifies that the selector for this Client will be visible even if off-line on a VCOM Control Panel that is configured to hide the off-line selectors. It is generally used for VCOM Device Interface clients that should, under normal operation, never go off-line thus allowing VCOM Control Panel operators to more easily notice an unanticipated disconnect event.
Latch Disable Talk Selector: Select to operate associated selector as a momentary, meaning that an audio path will only persist as long as the selector is clicked and held. Party Line Operation: This specifies that a given client operates like a Party Line. This means that anyone talking to that client will also talk to anyone listening to that client and anyone listening to that client will also hear everyone talking to that client.
IFB Destination: Designates a client as an IFB Destination that causes the system to interrupt any assigned listen or program feeds to the destination when a Control Panel initiates a talk path to the destination. This setting is typically used with on-air talent who need to be constantly monitoring the on-air program feed but periodically take cues from the director or producer.
ISO Destination: Designates a client as an ISO Destination that causes the system to interrupt any assigned listen or program feeds to the destination when a Control Panel initiates a talk path to the destination and automatically activates a return talk path from the destination back to the Control Panel. Additionally, the talk paths in both directions are isolated so that the conversation is kept private. This setting is typically used with cameras when the director or producer needs to isolate a particular camera from the camera PL to provide private instruction.
Allow Assignment to Multiple Party Lines: Allows a client to be remotely assigned to Party Lines through Party Line Assignment Mode.
Standard System Administration Privileges: Gives System Administrator privileges to the client.
Master System Administration Privileges: Gives Master System administrator privileges to the client.
Selector Assignment Restrictions No local Assignment By Administrator: This prohibits local assignments to be made by an Administrator. Assignments can only be done through the System Administration application
No Local Assignment By User: This prohibits local assignments to be made by a User. Assignments can only be made by an administrator from the System Administration application
Selector Assignments
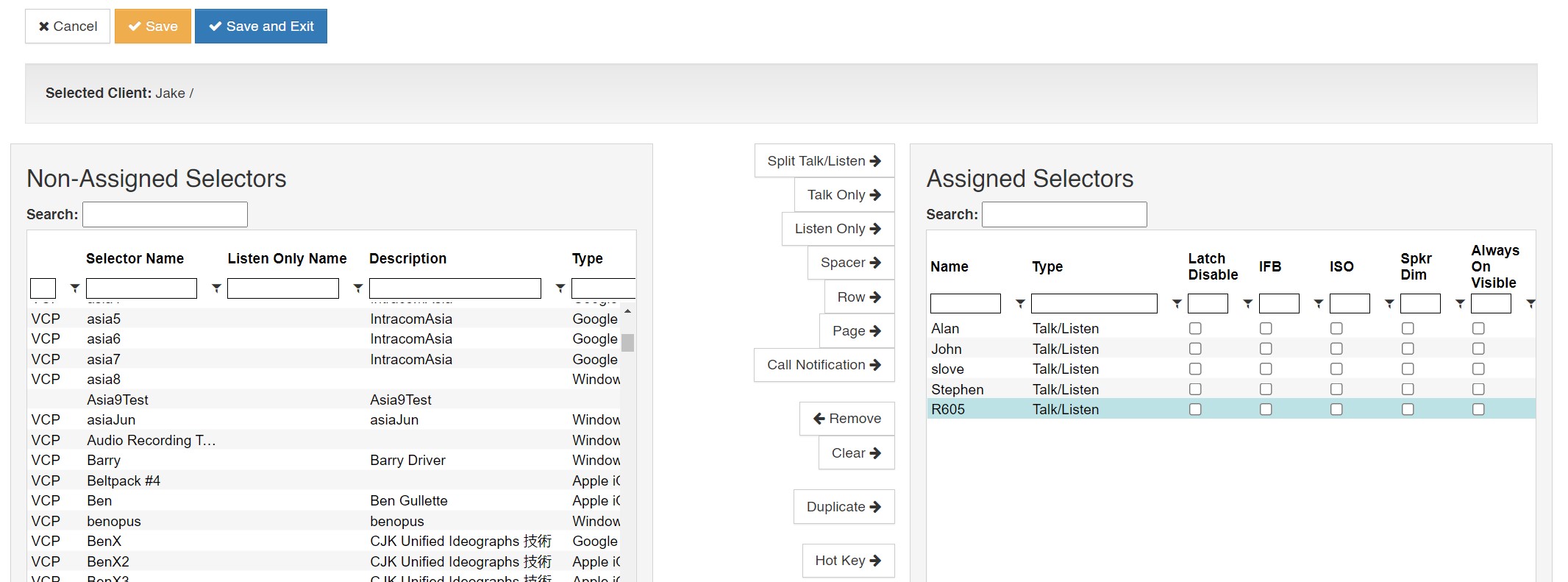
This page allows assignment of a Control Panel’s selectors. Highlight a selector in the left-hand portion of the screen and select one of the configuration options listed below.
Split Talk/Listen: Add the desired selector with both talk and listen paths.
Talk Only: Add the desired selector with only a talk path.
Listen Only: Add the desired selector with a Listen only path.
Remove: Highlight a selector in the right-hand portion of the screen and select ‘Remove’ to delete an assigned selector.
Clear: Delete all assigned selectors.
Hot Key: Assigns a keyboard key to the selected Selector so that the key can be used to activate and deactivate the Selector on a VCOM Control Panel. This option is only supported on the VCOM Control Panel for Windows.
Audio Settings
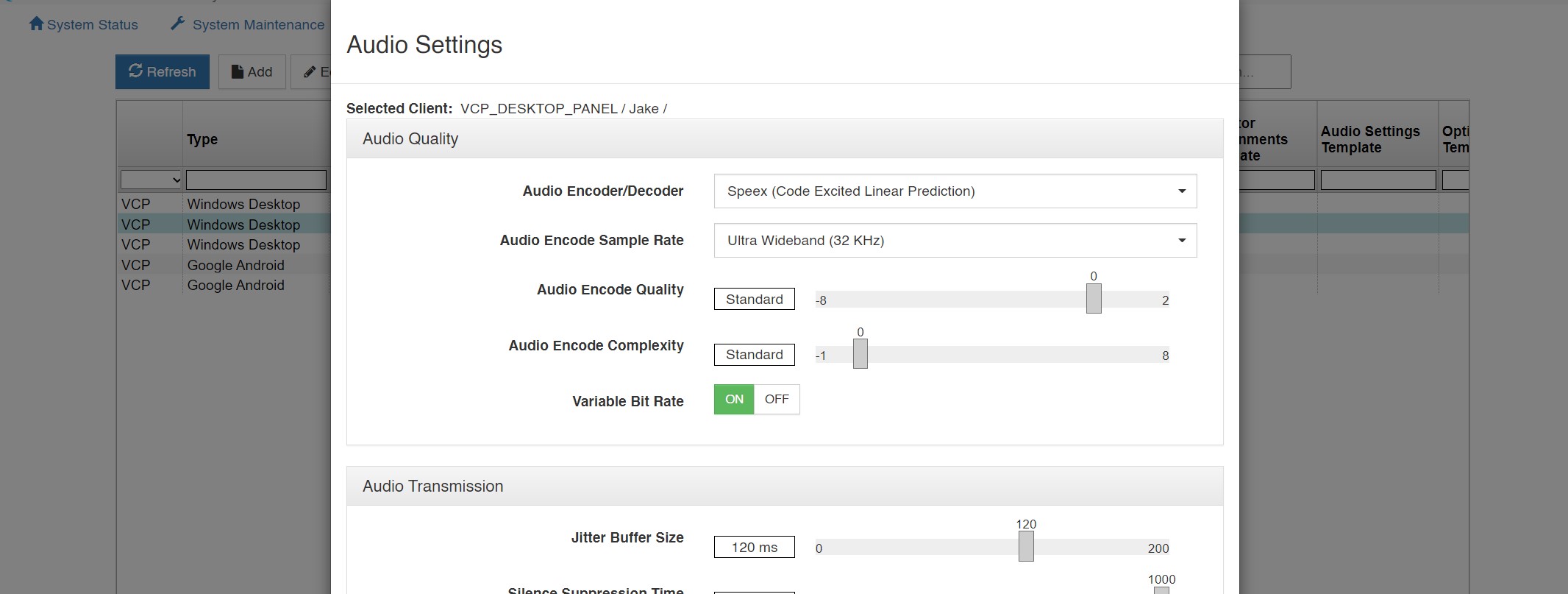
Audio Quality Audio Encoder/Decoder: This setting allows selection of a different encoder/decoder. For VCOM Control Panels and VCOM Device Interface clients the choice is between a High Compression / Low Bitrate Codec used for Internet connectivity and a Low Compression / High Bitrate codec that may be used for Local Network connectivity to slightly reduce latency. For SIP Devices the codec specified is preferential codec used when negotiating which codec to use with the SIP Device.
Audio Encode Sample Rate: This setting controls the sampling rate supported by the Clients and thereby dictates default fidelity for the Client connections. This setting is typically the same as the System Audio Sampling rate however it can be specified at lower rate but never at a higher rate (refer to System Audio Sampling Rate for additional detail). Higher audio sampling rates have more significant requirements in computational speed and network bandwidth. Careful consideration must be given when choosing this setting with respect to client hardware and the client network connection.
Audio Encode Quality: The VCOM System codec achieves compression at the expense of fidelity of the input speech signal. Unlike some other speech codecs, it is possible to control the tradeoff made between quality and bit-rate. Audio Encode Complexity: With the VCOM System codec, it is possible to vary the complexity allowed for the encoder. This is done by controlling how the search is performed with an integer ranging from 1 to 10. For normal use, the noise level at complexity 1 is between 1 and 2 dB higher than at complexity 10, but the CPU requirements for complexity 10 is about 5 times higher than for complexity 1. In practice, the best trade-off is between complexity 2 and 4, though higher settings are often useful when encoding non-speech sounds.
Audio Transmission
Variable Bit Rate: Allows the system’s codec to dynamically change the bit rate at which audio is being encoded. As sounds like vowels require a higher bit rate to achieve good quality as compared to “s” and “f” sounds, this setting efficiently achieves the best sound quality within the given confines. The system can be set for variable rate or fixed rate. While this setting improves the quality of speech, it conversely degrades the quality of music and should therefore be disabled when using a program feed. Jitter Buffer Size: This setting specifies the depth of the jitter buffer in milliseconds. In network-based communications, the delivery time of audio packets across the network may not be uniform. This characteristic is known as jitter. As such, audio received from a network connection must be buffered to compensate for this so that a continuous, time-relative stream of audio can be delivered to the consumer of the audio. Different network topologies will have different jitter characteristics. For example, a public Internet connection will have significantly more jitter than an internal local network. The effect of a jitter buffer that is too small will result in audio gaps. The value is specified in milliseconds.
Silence Suppression Time: Ceases all transmission of audio data when no voice activity is detected from a Control Panel or Device Interface after the specified time lapse. This virtually eliminates background noise during multiparty conferences. However, it may initially be disconcerting to some individuals as the ‘comfort noise’ typically associated with analog systems is suppressed. Additionally, this feature minimizes the overall required network bandwidth. The value is specified in milliseconds in the range of 100- 1000 ms or can be turned off entirely.
Packet Re-sequencer Depth: This setting specifies the number of packets that are stored when waiting for an out of sequence audio packet. In some network topologies, even if UDP packets are sent in sequential order, they are received non-sequentially. These packets must be re-sequenced before use. After the maximum re-sequencer depth has been reached, the packet being awaited is declared to be lost and the re- sequencing is re-started at the next earliest received packet. Valid settings are from 2 to 10 packets.
Audio Processing
Automatic Gain Control (AGC): This setting enables or disables AGC on the audio path
from Client to the Server. AGC automatically increases or decreases the audio level
such that the client presents a uniform audio level to the Virtual Matrix. AGC is primarily
appropriate for use with a Control Panel when used with a headset microphone. In
some situations where there is a high amount of background noise or some return
audio leakage the AGC may incorrectly amplify the noise to normal audio levels.
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Level: This setting increases or decreases the sensitivity of the AGC. Increasing or decreasing the sensitivity of the ACG changes the behavior of the AGC such that it adapts faster or slower, respectively, to audio levels not considered to be at uniform level. Decreasing the sensitivity may be useful in cases where there is a high amount of background noise or some return audio leakage.
Audio Input Level Gain (Pre-Mix): This setting controls the audio input level sent from the Client to the Virtual Matrix. This setting is typically used only when the client’s audio input device does not provide a sufficiently audible level (as heard by all other clients) and does not have a local gain control to compensate. The value can be adjusted a maximum of +/-18dB in 6dB steps.
Audio Output Level Gain (Post-Mix): This setting controls the audio output level sent to the Client from the Virtual Matrix. This setting is typically used only when the client’s audio output device does not provide a sufficiently audible level and does not have a local gain control to compensate. The value can be adjusted a maximum of +/-18dB in 6dB steps.
Speakerphone Speaker Dim Reduction: This setting dims the incoming audio output by a configured amount when you activate the talk key.
Echo Cancellation: This setting enables or disables the client’s Echo Cancellation. Echo Cancellation is useful if there is any return audio leakage from the client’s speaker back to his microphone. This may result in an audible echo heard by any other client that is talking and listening to the client with the return audio leakage.
Echo Cancellation Tail Length: This setting controls the duration the echo canceller waits to receive the echo before it begins the cancellation process. The recommended tail length is approximately a third of the room reverberation time. For example, in a small room, reverberation time is in the order of 300ms, so a tail length of 100ms is recommended.
Audio Encryption: This setting is a licensable option for security measures. Clients may choose from following options: No Encryption, AES 128, or AES 256.
VCOM Client Configuration Options
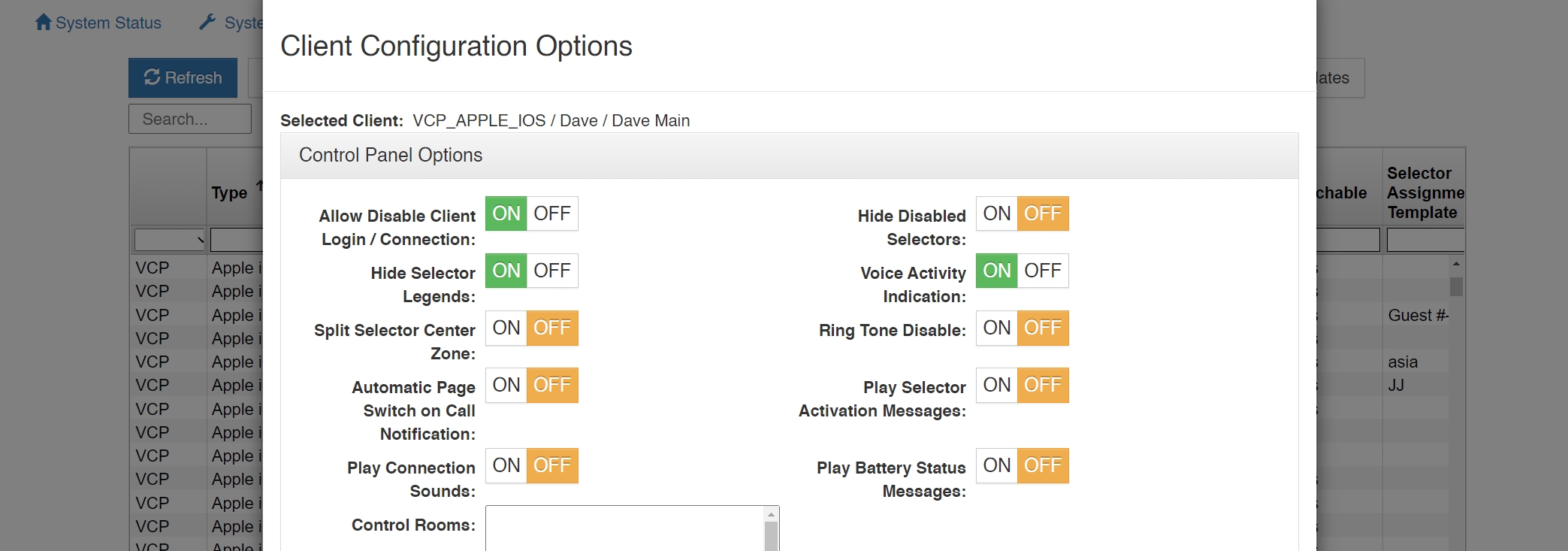
Control Panel Options
Allow Disable Client Login/Connection: This setting allows the client’s login capability
to be disabled.
Hide Disabled Selectors: This setting hides selectors assigned to other clients that are not logged into the system. When the clients come online, their selector will dynamically appear.
Hide Selector Legends: This setting hides the overlaid selector legends displayed on listen selectors (‘L’) and talk selectors (‘T’).
Voice Activity Indication: This setting is used to visually indicate voice activity on Control Panel selectors, represented by selector text and background color switching between base state (yellow text / navy background) and default activity indication colors (white text / light navy background) or selected activity indication colors (variable). Voice Activity Indication is only available if the Control Panel has the ability to listen to or is being talked to by the client indicating voice activity. Split Selector Center Zone: This setting allows the center of the selector to be used to activate both the talk and listen selectors for split talk/listen selectors.
Ring Tone Disable: Disables Ring Tone loaded in SIP Client Options for the selected user.
Automatic Page Switch on Call Notification: This setting will cause the pages (when multiple pages are used) to switch to the page with the current incoming call from another user.
Play Selector Activation Messages: This setting will cause the unit to announce “Talk on/ Talk Off” or “Listen On/Off” when activating the selectors.
Play Connection Sounds: This setting will cause the unit to play a sound every time you connect or disconnect to the network.
Play Battery Status Messages: This setting will announce the status of the battery depending on the percentage of battery left – (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30)
Control Panel Function Buttons
Enable Party Line Assignment Button: This will enable the PL Assignment button on the
Control Panel allowing the user the capability of assigning other “devices” to PLs.
Enable Selector Volume Buttons: This enables the “Selector Volume” button that gives the user a quick key to adjust individual selector volumes.
Enable Dial Pad Button: This enables a button that enables the Dial Pad when a SIP device is being accessed to dial out.
Enable Selector Assignment Button: This enables a button that gives the user the capability of assigning selectors through the VCP GUI via a pop-up window.
Enable Selector Relocation Button: This enables a button that allows the user to rearrange the order of their selectors to customize to their particular needs.
Enable Reveal Inactive Selectors Button: This allows the user to disable/enable inactive (not logged in) selectors.
Enable Launch Geo Mapping Button: This enables a button that will launch a web page directed to the Geo Mapping Server to display the Geo Mapping web application.
Control Panel for iOS Options
Restart in Background if Previously Active: This will restart the VCP in the background
when the device is restarted.
Operate as a Beltpack: This will use the “Beltpack Template” that allows for oversized buttons on an iOS device such as the iPhone/iPod Touch which can also be used with Screen covers with cutouts for these oversized buttons.
Disable Integrated Mic and Speaker: This will disable the use of an internal mic and speaker on the iOS device.
Control Panel/Device Interface Options Voice Activity Detection Time in Ms: This allows the amount of time to be set for Voice Activity Detection to turn on for the selected user.
Geo Mapping
Geo Mapping Disable: This will disable the selected user’s access and data sent to the
Geo Mapping server.
Geo Mapping Latitude/Longitude: This allows the GPS coordinates of the selected user to be set when used as a fixed position. This is not used for mobile devices.
SIP Client Configuration Options
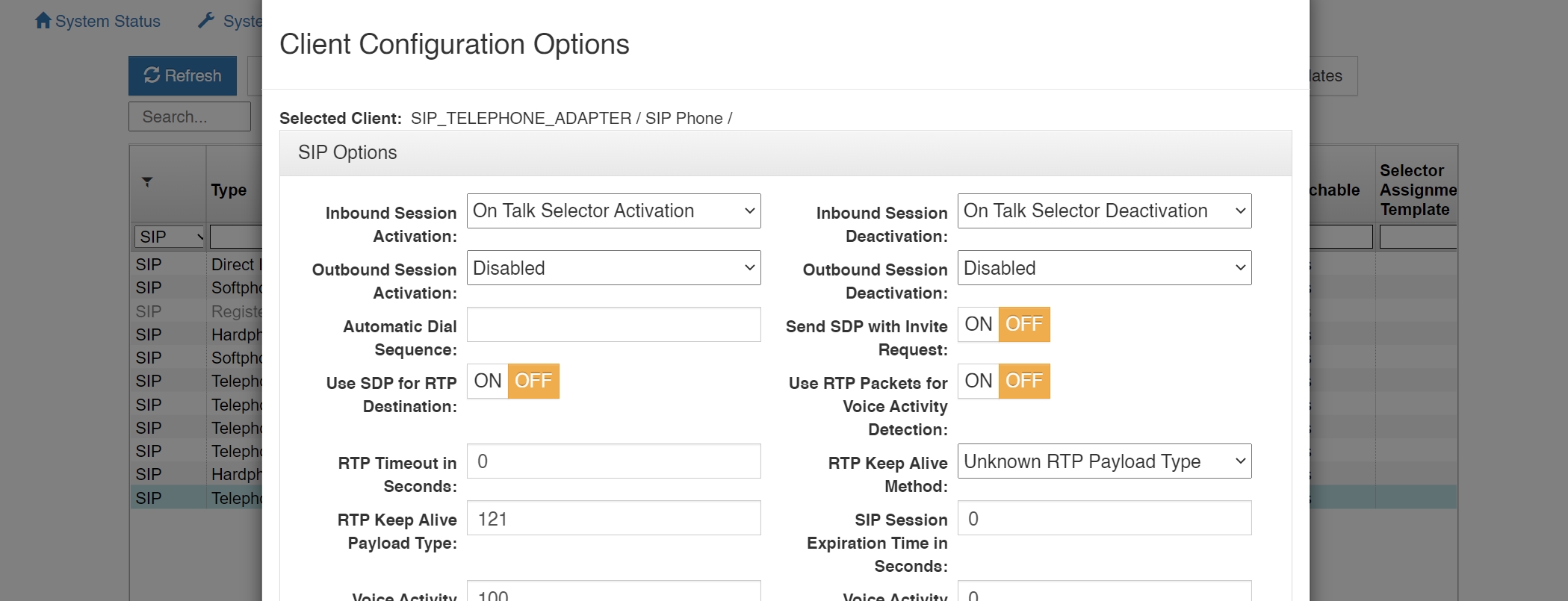
Inbound Session Activation: This setting specifies how the Virtual Matrix handles the activation of a call initiated by the SIP client. If configured for ‘Disabled,’ the call initiated by the SIP client is ignored. If configured for ‘On Call Received (Auto Answer),’ the call initiated by the SIP client will be automatically answered by the VCOM Virtual Matrix. If configured for ‘On Talk Selector Activation,’ the call initiated by the SIP Client will be indicated on the associated Control Panel selectors and the call will be answer only if a VCOM Control Panel activates the talk selector associated with the SIP Client.
Inbound Session Deactivation: This setting specifies how the Virtual Matrix handles the deactivation of a call initiated by the SIP client. If configured for ‘Disabled,’ the call initiated by the SIP client can never be disconnected by the Virtual Matrix. If configured for ‘On Forced Disconnect,’ the call initiated by the SIP client can only be disconnected by a VCOM Control Panel using the ‘Disable Client Login’ feature. If configured for ‘On Talk Selector Deactivation,’ the call initiated by the SIP Client will be disconnected when all VCOM Control Panels deactivate the talk selectors associated with the SIP Client.
Outbound Session Activation: This setting specifies how the Virtual Matrix handles the activation of a call initiated to the SIP client. If configured for ‘Disabled,’ the Virtual Matrix cannot initiate any call to the SIP client. If configured for ‘On Registration,’ the Virtual Matrix will initiate a call to the SIP client as soon as the SIP client makes its presence known through a process known as ‘Registration.’ If configured for ‘On Talk Selector Activation,’ the Virtual Matrix will initiate a call to the SIP client when any VCOM Control Panel activates the talk selector associated with the SIP Client.
Outbound Session Deactivation: This setting specifies how the Virtual Matrix handles the deactivation of a call initiated to the SIP client. If configured for ‘Disabled,’ the call initiated to the SIP client can never be disconnected by the Virtual Matrix. If configured for ‘On Forced Disconnect,’ the call initiated to the SIP client can only be disconnected by a VCOM Control Panel using the ‘Disable Client Login’ feature. If configured for ‘On Talk Selector Deactivation,’ the call initiated to the SIP Client will be disconnected when all VCOM Control Panels deactivate the talk selectors associated with the SIP Client.
Automatic Dial Sequence: This setting specifies a dial sequence to be dialed as soon a call is established with a SIP Client. To insert a delay in the dial sequence, use ‘P’ to insert a 5 second delay and ‘p’ to insert a 1 second delay.
Send SDP With Invite Request: This setting changes the default behavior of calls initiated by the Virtual Matrix to allow compatibility with devices that do not conform to proper SIP implementation, specifically the Raytheon ARA-1. Normally when the Virtual Matrix initiates a call to the SIP client, it does so without sending a Session Description Protocol (SDP), so that it can subsequently control the codec selection.
Use SDP for RTP Destination: This setting changes the default behavior of the Virtual Matrix to allow strict conformance with the Real-Time Protocol specification. Normally the Virtual Matrix ignores the RTP IP address specified in the SDP and uses the actually received RTP IP address as the SIP specification as written and does not account for SIP clients behind NAT firewalls that typically alter the IP address of the packet.
Use RTP Packets for Voice Activity Detection: Many SIP device employ Silence Suppression to eliminate unnecessary network traffic. When a device supports silence suppression, this option can be enabled such that Voice Activity will be indicated whenever RTP audio packets are received. If this option is not enabled, The Virtual Matrix will indicate Voice Activity by analyzing the content of the audio stream.
RTP Timeout In Seconds: During an active SIP call, there should be a constant and ongoing flow of RTP audio packets or RTP Keep Alive packets between the client and the server in additional to the SIP control packets. In some cases the RTP audio packets might be blocked even though the SIP control packets are not. This option specifies the time in seconds to wait for RTP audio packets before assuming there must be a problem with the connection and disconnecting the call. Setting this value to zero disables the check for an RTP Timeout.
RTP Keep Alive Method: When a SIP device supports silence suppression, it is often necessary to send RTP keep alive packets when audio is not being sent in order to ensure that no firewalls or routers in between close the associated ports due to inactivity. This option specifies the type of RTP Keep Alive Method as not all SIP devices can accept the RTP Keep Alive Methods specified by RFC 6223.
SIP Session Expiration Time In Seconds: During an active SIP call there is often a constant and ongoing flow of SIP control packets between the client and the server. In some cases the SIP control packets might stop due to a loss of network connectivity. This option specifies the time in seconds to wait for the SIP control packets before assuming there must be a problem with the connection and disconnecting the call. Setting this value to zero disables the check for a SIP Session Expiration.
Voice Activity Detection Validation Time in Ms: This allows the amount of time to be set for Validation Time to register as a Voice Activity event. For example, there needs to be 100ms of audio for Voice Activity Detection to turn on to pass audio in the picture above.
Voice Activity Detection Off Delay Time in Ms: This allows the amount of time to be set for Voice Activity Detection to be turned off. This is the amount of silence allowed after a user is speaking.
Call Notification Ring Tone: A file path can load an audio file to be played when an incoming call is placed.
Auto-Answer Notification Message: This option allows the selection of an audio wave file to be played as the notification message to the caller to indicate that the connection has been established between the SIP client and the VCOM Virtual Matrix. User provided files can be uploaded to the server provided the files are in a 16 bit mono audio format, preferably set to the same Audio Mix Sample Rate of the Virtual Matrix.
Auto-Answer Delay Time In Ms: This option sets the delay time in milliseconds after which the VCOM Virtual Matrix will automatically answer a received SIP call. Typically this value will be set to zero such that the call is answered immediately. In some situations it is desirable to delay answering the call so that VCOM Control Panels listening to that line will hear a ring signal.
Auto-Answer Access Code: This option enables the requirement that an Access Code must be entered by the caller if the VCOM Virtual Matrix automatically answers a received SIP call. The Access Code may consist of up to 10 digits. When configuring an access code, it is recommended to configure an appropriate Auto-Answer Notification Message which prompts the caller to enter the access code. The provided "AccessCode.wav" message is provided for this purpose.
Use 16kHz for G.722 Timestamp: Sets bandwidth to 16kHz when the G.722 CODEC is used.
Internal SIP Client User Name Prefix: Character placed before the Client’s User Name when dialing, most commonly used is the asterisk.
SIP Direct IP Trunk and Registered Trunk Options
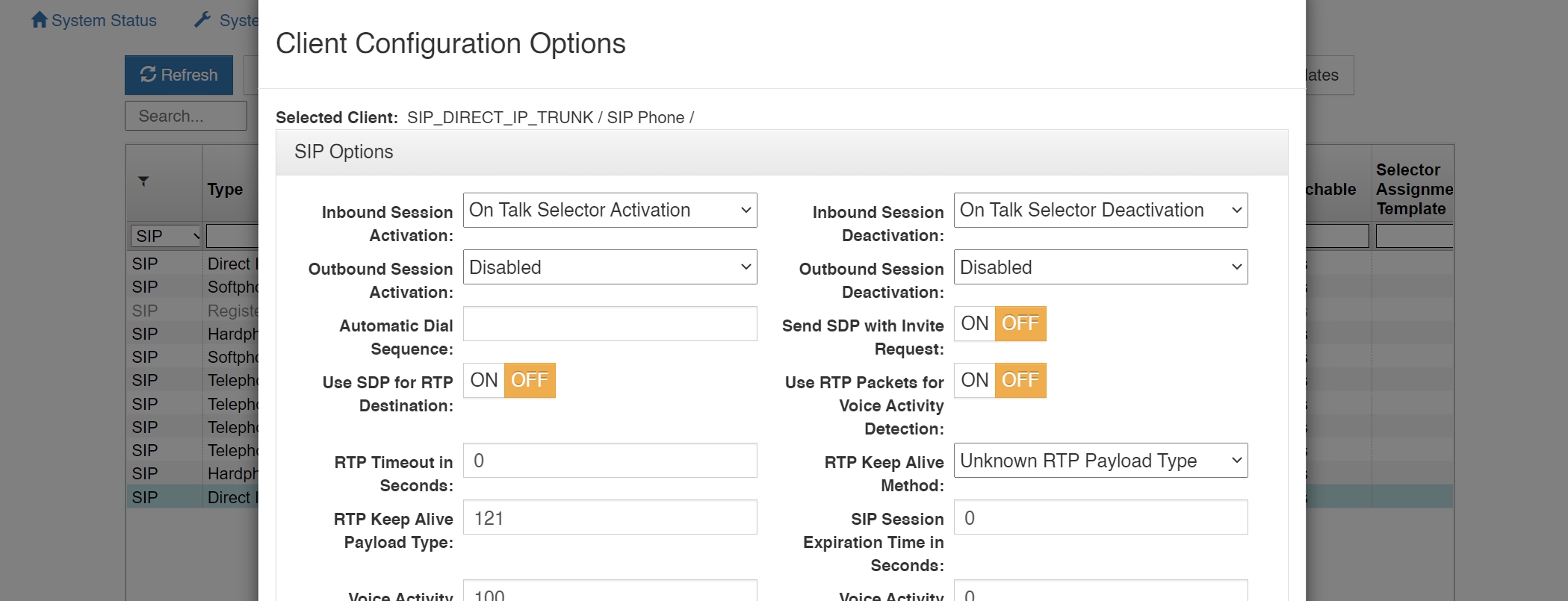
In most situations, the VCOM Virtual Matrix itself acts as the SIP Registrar and SIP Server for SIP Clients to connect to it. However, when connecting to other SIP Registrars and SIP Servers, the VCOM Virtual Matrix can itself act as a SIP Client when a client is configured as a SIP Direct IP Trunk or a SIP Registered Trunk using the following options:
SIP Target User Name: This specifies the fixed user name to use as the Address of Record (AOR) when sending SIP registration and/or SIP invite requests. If using a VCOM Control Panel to dial out through a PBX, this field must be left blank, as the dialed phone number will be User Name.
SIP Target Primary Host Name: This specifies the target primary host name or IP address of the target SIP Registrar or SIP Server to use when sending SIP registration and SIP invite requests.
SIP Target Secondary Host Name: This specifies the target secondary host name or IP address of the target SIP Registrar or SIP Server to use when sending SIP registration and/or SIP invites. The secondary host name will only be used in the case where a secondary (failover) server is available and the primary server is not reachable. If no secondary (failover) server is available, this field must be left blank.
SIP Target Proxy Server IP Address (optional): This specifies the IP address of the SIP Proxy, if a SIP Proxy is used.
SIP Registration Expiration Time In Seconds: This option specifies the time in seconds that the Virtual Matrix is expected to refresh the registration with the target SIP Registrar. If the registration is not refreshed with the specified time frame, the SIP session will be terminated.
STUN Server or Proxy IP Address: This option enables SIP client transversal through a NAT by specifying the IP address of a STUN Server which will inform the Virtual Matrix of the public IP address of the SIP Client so that it can be included when sending SIP registration and SIP invite requests.
Geo Mapping
Geo Mapping Disable: Check this box to disable the use of geo mapping on any
given SIP periphery
Geo Mapping Latitude (Fixed Position): Input the fixed latitude position for a geographically static SIP periphery.
Templates
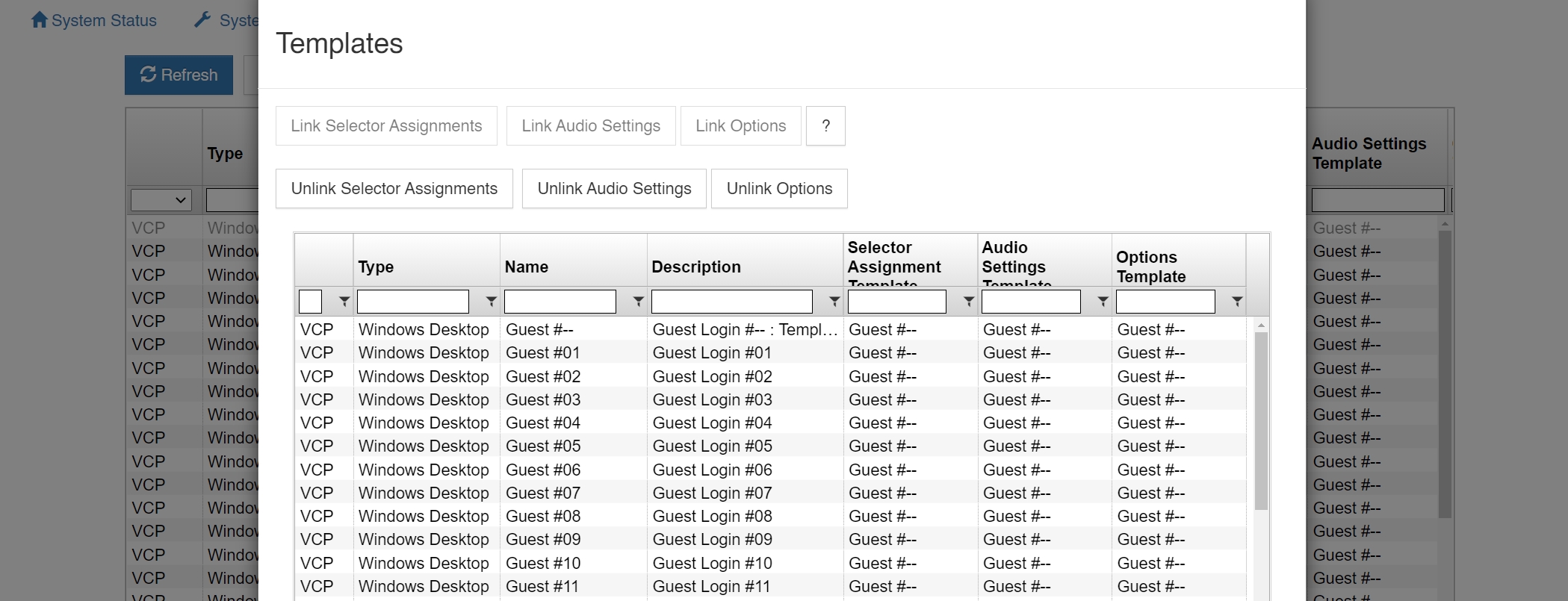
Templates allow you to apply a given client’s selector assignments, audio settings, and/or options to one or more other clients.
First select the client you want to use as the template and then using the CTRL key, select one or more other clients you want to apply your template’s settings to. You will see the Templates section become enabled. Click on the appropriate Link button to populate selector assignments, audio settings, and/or options from your template to your other selected clients. If you later want to remove applied client settings from your template, use the appropriate Unlink button.